oracle Application Express (APEX) is a rapid web application
development tool for Oracle database. Before building or running apex
application, there are few concepts and terminology you need to
familiarize with. The outline of this article is to cover
Assuming that you already have account in apex.oracle.com (If you don't, please follow instructions from APEX Introduction article), go to login page of apex.oracle.com and enter workspace name, user name and password.

You are given Workspace Administrator role for oracle.apex.com account. Once you login successfully, home page looks similar to below screenshot.

Most part of development time is spent in Application Builder building pages, applications or SQL Workshop running queries. SQL Workshop is self explanatory if you use SQL Developer or any SQL, PL/SQL interface tool. I will focus mainly on Application Builder.
Application Builder Concepts
Application Builder has collection of apex applications. Your oracle.apex.com account comes with a sample application. You can run or modify this application.

The following terminology are important to know when working with Application Builder:
Running sample application
By default you have a sample application in your workspace. It can be used to demonstrate various features offered by Application Express like charts, reports, forms, etc., Run the sample application by clicking on 'Run Application' icon as shown in above screenshot. In the login name, enter user name as demo (or) admin with password as your workspace name in lower case.

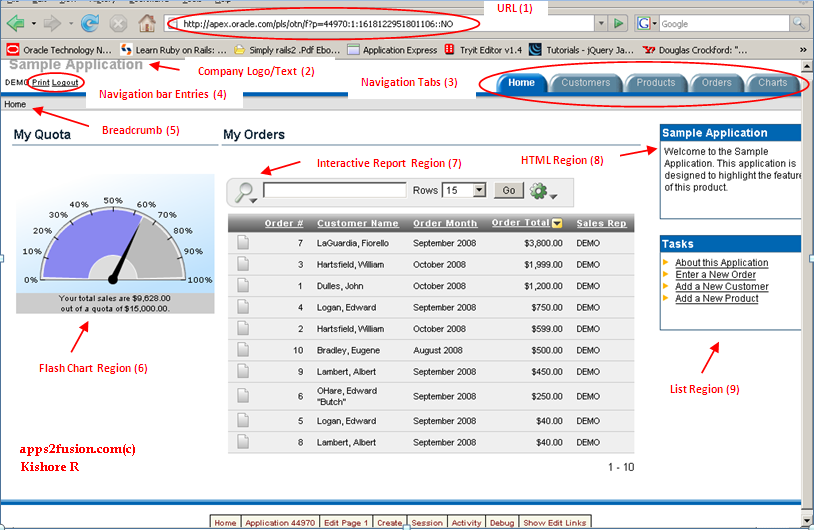
Home
page alone shows a lot of information about Application Express
features. The following are the pointers from the above screenshot.
1. URL of the page. Every page in apex is accessed through browser URL, but authorization schemes control user access. Authorization schemes can be specified for an entire application, a page, or a specific page control such a region, item or button. For example, you could use an authorization scheme to selectively determine which tabs, regions, or navigation bar entries a user sees.
URL of the home page was http://apex.oracle.com/pls/otn/f?p=44970:1:1618122951801106::NO
It includes important information about application, page, session and few more. I will cover in detail in later section.
2. Company logo/text is an attribute of Application definition. It appears on all pages in application. You can use an image or text.
3. Navigation tabs simplifies navigation to specific pages. Type of tabs (One-Level /Two-Level / None) is defined while creating application. Sample application is using One-Level tabs. Graphical representation can be used when defining tabs. Tabs can be conditionally displayed as well.
4. Navigation bar entries provide hypertext based navigation. By default it has Print and Logout entries. Placement (right / left) is determined by page templates.
5. Breadcrumb provide hierarchical navigation to any number of levels. Clicking on breadcrumb entry is associated with a page and also a parent page. Breadcrumb builds up with breadcrumb entries the deeper the user navigates to the pages. Try navigating to Add/Modify customers page by clicking on create button in Customers page, breadcrumb now shows 'Home > Customers > Add/Modify Customers' with hyper links to parent breadcrumb entries i.e. Home, Customers.
Breadcrumb adds another level for easy navigation between pages. You are familiar with it in Oracle EBS Self-Service modules.
6,7,8,9. Home page has four regions (My Quota, My Orders, Sample Application and Tasks). Each region uses different region type. My Quota demonstrates the use of Flash Dial Chart. My Orders is an interactive report which is a feature introduced in Apex 3.1. Both of these regions are based of SQL query. Sample Application region is HTML with simple text. Tasks is a list region using navigation list to branch on other pages in the application.
Interactive report gives users a plethora of personalization options like adding filters, computations, highlight columns based on conditions, save report, search by column values etc.
You can play around with Sample application to get a feel of APEX's rich features. One of the prominent feature is ease of navigation for end users using breadcrumbs, navigation tabs, drill down column links, navigation lists etc.
Once you get a hang of pages and navigation, you can look at how a page is defined by clicking 'Edit Page 1' link at the bottom of the page (or) navigating from Application Builder > Sample Application > 1 - Sample Application page.
Page Definition:
The page definition is divided into three main sections:
The Application Express engine dynamically renders and processes pages based on data stored in Oracle database tables. To view a rendered version of your application, you request it from the Application Express engine. When you run an application, the Application Express engine relies on two processes.
When you request a page using a URL, the engine is running Show Page. When you submit a page, the Application Express engine is running Accept Page or performing page processing during which it saves the submitted values in the session cache and then performs any computations, validations, or processes.

Page Rendering:
Each page is associated with attributes such as name, title, template, etc. In the above screenshot page template used is 'Application Default'. It is the default page template attached to application. You can check template name by going to Shared Components (second icon on top right navigation) > Application Definition > Template Defaults (section). Application Default is substituted with One Level Tabs template.
Page template defines how header, body and footer sections of the page are displayed. It has bunch of HTML tags with Substitution Strings. When the page is rendered, Application Engine replaces substitution string with actual value. Substitution strings alone takes an article to explain them in detail.
Regions are the actual containers of items in a page. Region type determines the source of the region whether it is flash chart, form, report, HTML etc. Source field of the region has either SQL query or HTML depending on region type. Region Display point determines where a region is displayed on the page. They are available depending on the page template.
Items are basic building blocks of a page. They are variety of item types to choose from such as check box, text box, radio button, display item, hidden item, etc.
Computations and Processes can have PL/SQL block for assigning values to items in the page. You can also specify at what point the logic should be executed like On Page Load, Before header. These are like triggers in Forms 6i.
Page Processing:

Understanding URL syntax is useful when defining navigation to pages using navigation lists or hypertext links. I will cover more on this in coming article. There is so much ground to cover in Application Express, once you start building applications apex is mostly wizard driven and really simple.
In the coming articles, I will do tutorials possibly video tutorial to build a simple application for searching, creating, updating and deleting Person details.
- Understanding User roles
- Components in Application Express
- Useful Terminology in APEX
- Running Sample application
- Understanding APEX URL Syntax
Assuming that you already have account in apex.oracle.com (If you don't, please follow instructions from APEX Introduction article), go to login page of apex.oracle.com and enter workspace name, user name and password.

Once
you login successfully, home page shows different components of APEX
depending upon user role assigned to you. Users are divided into four
primary roles:
- Developers are users who create or edit applications
- Workspace Administrators are users who perform administration tasks specific to workspace like managing user accounts, services and monitoring workspace activity
- Oracle APEX Administrators are superusers that manage an entire hosted instance using the Application Express Administration Services application.
- End Users have no development privileges
You are given Workspace Administrator role for oracle.apex.com account. Once you login successfully, home page looks similar to below screenshot.

You
are presented with different icons, navigation tabs and regions on the
right which shows useful information about your workspace. Region at the
bottom of the home page shows Apex Version (v3.2.0.00.27 for oracle
apex site), apex workspace and user name. Workspace Schema (in my case
'BT_APEX') is database schema attached to your apex workspace.
Four components which are of interest to us are Application Builder, SQL Workshop, Utilities and Administration.
Four components which are of interest to us are Application Builder, SQL Workshop, Utilities and Administration.
- Application Builder is where you build apex applications. You can also import / export applications from sql files.
- SQL Workshop is like web version of SQL Developer. You can browse database objects in your schema, run SQL commands, create SQL scripts and use Query Builder to create a sql query using its GUI.
- Utilities has numerous useful tools for monitoring database, viewing meta data about APEX.
- Administration is used to manage sessions, caching, users and monitor activity.
Most part of development time is spent in Application Builder building pages, applications or SQL Workshop running queries. SQL Workshop is self explanatory if you use SQL Developer or any SQL, PL/SQL interface tool. I will focus mainly on Application Builder.
Application Builder Concepts
Application Builder has collection of apex applications. Your oracle.apex.com account comes with a sample application. You can run or modify this application.

The following terminology are important to know when working with Application Builder:
- Workspace: A workspace allows multiple developers to work within the same Oracle Application Express installation. It can be based on one or more database schemas. As a rule workspaces should be organized such that they contain applications that are related to each other.
- Application: It is a collection of pages and branches connecting them. Its attributes include authentication scheme, default UI templates. Application is synonymous to project in JDeveloper.
- Page: A page is the basic building block of an application. When you build an application in Application Builder, you create pages that contain user interface elements, such as tabs, lists, buttons, items, and regions.
- Region: Content is displayed in regions, which are logical subsections of a page. Each page can have any number of regions of several different types. These types include: HTML text, SQL Queries, PL/SQL-generated HTML, and charts. Each region is rendered using a region template. Regions are positioned on the page using display points defined in the page template.
- Item: An item can be a text field, text area, password, select list, check box, and so on. Item attributes affect the display and behavior of items on a page. For example, these attributes can impact where a label displays, how large an item is, and whether or not the item is displayed next to, or below the previous item. The value of an item is automatically stored into the application's session state, which can be referenced at any point within the user's session.
Running sample application
By default you have a sample application in your workspace. It can be used to demonstrate various features offered by Application Express like charts, reports, forms, etc., Run the sample application by clicking on 'Run Application' icon as shown in above screenshot. In the login name, enter user name as demo (or) admin with password as your workspace name in lower case.

Sample
application shows an easy-to-use interface for viewing, updating, and
searching order and customer information for electronic and computer
products. Users can navigate among the pages using the Home, Customers,
Products, Orders and Charts tabs.

1. URL of the page. Every page in apex is accessed through browser URL, but authorization schemes control user access. Authorization schemes can be specified for an entire application, a page, or a specific page control such a region, item or button. For example, you could use an authorization scheme to selectively determine which tabs, regions, or navigation bar entries a user sees.
URL of the home page was http://apex.oracle.com/pls/otn/f?p=44970:1:1618122951801106::NO
It includes important information about application, page, session and few more. I will cover in detail in later section.
2. Company logo/text is an attribute of Application definition. It appears on all pages in application. You can use an image or text.
3. Navigation tabs simplifies navigation to specific pages. Type of tabs (One-Level /Two-Level / None) is defined while creating application. Sample application is using One-Level tabs. Graphical representation can be used when defining tabs. Tabs can be conditionally displayed as well.
4. Navigation bar entries provide hypertext based navigation. By default it has Print and Logout entries. Placement (right / left) is determined by page templates.
5. Breadcrumb provide hierarchical navigation to any number of levels. Clicking on breadcrumb entry is associated with a page and also a parent page. Breadcrumb builds up with breadcrumb entries the deeper the user navigates to the pages. Try navigating to Add/Modify customers page by clicking on create button in Customers page, breadcrumb now shows 'Home > Customers > Add/Modify Customers' with hyper links to parent breadcrumb entries i.e. Home, Customers.
Breadcrumb adds another level for easy navigation between pages. You are familiar with it in Oracle EBS Self-Service modules.
6,7,8,9. Home page has four regions (My Quota, My Orders, Sample Application and Tasks). Each region uses different region type. My Quota demonstrates the use of Flash Dial Chart. My Orders is an interactive report which is a feature introduced in Apex 3.1. Both of these regions are based of SQL query. Sample Application region is HTML with simple text. Tasks is a list region using navigation list to branch on other pages in the application.
Interactive report gives users a plethora of personalization options like adding filters, computations, highlight columns based on conditions, save report, search by column values etc.
You can play around with Sample application to get a feel of APEX's rich features. One of the prominent feature is ease of navigation for end users using breadcrumbs, navigation tabs, drill down column links, navigation lists etc.
Once you get a hang of pages and navigation, you can look at how a page is defined by clicking 'Edit Page 1' link at the bottom of the page (or) navigating from Application Builder > Sample Application > 1 - Sample Application page.
Page Definition:
The page definition is divided into three main sections:
- Page Rendering lists user interface controls and logic that are executed when a page is rendered. Page Rendering is the process of generating a page from the database.
- Page Processing lists logic controls like computations, processes that are evaluated or executed when page is processed.
- Shared Components lists common components that are used by one or more pages within the application.
The Application Express engine dynamically renders and processes pages based on data stored in Oracle database tables. To view a rendered version of your application, you request it from the Application Express engine. When you run an application, the Application Express engine relies on two processes.
- Show Page is the page rendering process. It assembles all the page attributes (including regions, items, and buttons) into a viewable HTML page.
- Accept Page performs page processing. It performs any computations, validations, processes, and branching.
When you request a page using a URL, the engine is running Show Page. When you submit a page, the Application Express engine is running Accept Page or performing page processing during which it saves the submitted values in the session cache and then performs any computations, validations, or processes.

Page Rendering:
Each page is associated with attributes such as name, title, template, etc. In the above screenshot page template used is 'Application Default'. It is the default page template attached to application. You can check template name by going to Shared Components (second icon on top right navigation) > Application Definition > Template Defaults (section). Application Default is substituted with One Level Tabs template.
Page template defines how header, body and footer sections of the page are displayed. It has bunch of HTML tags with Substitution Strings. When the page is rendered, Application Engine replaces substitution string with actual value. Substitution strings alone takes an article to explain them in detail.
Regions are the actual containers of items in a page. Region type determines the source of the region whether it is flash chart, form, report, HTML etc. Source field of the region has either SQL query or HTML depending on region type. Region Display point determines where a region is displayed on the page. They are available depending on the page template.
Items are basic building blocks of a page. They are variety of item types to choose from such as check box, text box, radio button, display item, hidden item, etc.
Computations and Processes can have PL/SQL block for assigning values to items in the page. You can also specify at what point the logic should be executed like On Page Load, Before header. These are like triggers in Forms 6i.
Page Processing:
Validations
can be item-level or page-level. Branches define the navigation to
other pages depending on a event like a button click or Enter key etc.
Shared Components:
Shared
components are reusable components which are used by one or more pages.
Shared components section on the page shows all the shared components
that are referenced in that page.
Global Page (Page Zero):
Global Page (Page Zero):
When
an application is created, page zero is created by default. Page zero
components are rendered on every page. You can define regions, items and
buttons on page 0. Below screen shot of page zero in Sample Application
shows breadcrumb menu entry and chart list regions appear on every
page. Chart list is conditionally displayed. A condition is a small unit
of logic that helps you control the display of regions, items, buttons,
and tabs as well as the execution of processes, computations and
validations.

Understanding APEX URL Syntax
The URL that displays for each page identifies the location of Oracle Application Express, the address of Oracle Application Express, the application ID, the page number, and the session ID.
For Example, take the URL of Home page in Sample Application http://apex.oracle.com/pls/otn/f?p=44970:1:1618122951801106::NOThis example indicates:
The URL that displays for each page identifies the location of Oracle Application Express, the address of Oracle Application Express, the application ID, the page number, and the session ID.
For Example, take the URL of Home page in Sample Application http://apex.oracle.com/pls/otn/f?p=44970:1:1618122951801106::NOThis example indicates:
- apex.oracle.com is URL of server. It could like : when run in your environment.
- pls indicates apex is using mod_plsql cartridge. If your apex installation is based of pl/sql gateway
- otn is database access descriptor (DAD) name. DAD describes how HTTP Server connects to the database server so that it can fulfill an HTTP request. The default value is apex.
- f?p= is a prefix used by Oracle Application Express
- 44970 is application being called. You can also use Application alias rather than application id.
- 1 is the page within the application to be displayed
- 1618122951801106 is session number.
- NO is debug mode.
Understanding URL syntax is useful when defining navigation to pages using navigation lists or hypertext links. I will cover more on this in coming article. There is so much ground to cover in Application Express, once you start building applications apex is mostly wizard driven and really simple.
In the coming articles, I will do tutorials possibly video tutorial to build a simple application for searching, creating, updating and deleting Person details.
nice presentation about the oracle topic and good points were stated in the blog really a worth reading article.
ReplyDeleteCALFRE
presentation is too good and very interesting.
ReplyDeleteoracle fusion SCM on line training